
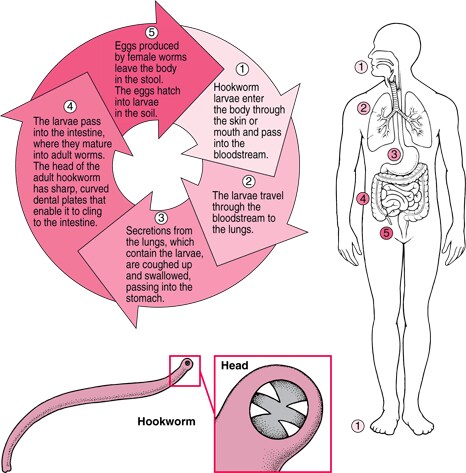
Trichinosis worms (whipworm): Trichinosis is the third most common roundworm that infects humans. They are usually less than half an inch long. Hookworms attach themselves to the walls of the small intestine with a hook and live there.
It is now being used free-of-charge as the sole tool in campaigns to eliminate both diseases globally. It was quickly discovered to be ideal in combating two of the world’s most devastating and disfiguring diseases which have plagued the world’s poor throughout the tropics for centuries. Originally introduced as a veterinary drug, it kills a wide range of internal and external parasites in commercial livestock and companion animals. Discovered in the late-1970s, the pioneering drug ivermectin, a dihydro derivative of avermectin—originating solely from a single microorganism isolated at the Kitasato Intitute, Tokyo, Japan from Japanese soil—has had an immeasurably beneficial impact in improving the lives and welfare of billions of people throughout the world. The larvae mature in the intestines.
There are few drugs that can seriously lay claim to the title of ‘Wonder drug’, penicillin and aspirin being two that have perhaps had greatest beneficial impact on the health and wellbeing of Mankind. Most studies have ignored the effects of parasitic protozoa (Blastocystis spp., Giardia intestinalis, Entamoeba spp., Cryptosporidium spp., etc.) and metazoa (roundworms, whipworms, pinworms, threadworms, hookworms, and tapeworms) on human BGM because of the unique characteristics of developed countries, where evolution is thought to have. This paper looks in depth at the events surrounding ivermectin’s passage from being a huge success in Animal Health into its widespread use in humans, a development which has led many to describe it as a “wonder” drug.Symptoms Ascariasis: The infection is caused by Ascaris lumbricoides roundworms and is typically found in tropical and sub-tropical areas.
When children are continuously infected by many worms, the loss of iron and protein can When it first appeared in the late-1970s, ivermectin, a derivative of avermectin (Fig. 1– 6) However, none have concentrated in detail on the interacting sequence of events involved in the passage of the drug into human use.The most serious effects of hookworm infection are the development of anemia and protein deficiency caused by blood loss at the site of the intestinal attachment of the adult worms. Several extensive reports, including reviews authored by us, have been published detailing the events behind the discovery, development and commercialization of the avermectins and ivermectin (22,23-dihydroavermectin B), as well as the donation of ivermectin and its use in combating Onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis.
Under the terms of the research agreement, researchers at the Kitasato Institute isolated organisms from soil samples and carried out preliminary in vitro evaluation of their bioactivity. In the early-1970s, a novel international Public Sector–Private Sector partnership was initiated by one of us (Ōmura, then head of the Antibiotics Research Group at Tokyo’s Kitasato Institute), forming a collaboration with the US-based Merck, Sharp and Dohme (MSD) pharmaceutical company. It was the world’s first endectocide, forerunner of a completely new class of antiparasitic agents, potently active against a wide range of internal and external nematodes and arthropods.
Indicative of the impact, in Brazil, where some 80% of the bovine herd is infested, losses total about $2 billion annually. 7– 12) Ivermectin is also highly effective against ticks, for example, the ixodid tick Rhipicephalus ( Boophilus) microplus, one of the most important cattle parasites in the tropics and subtropics, which causes enormous economic damage. It is effective against a wide range of parasites, including gastrointestinal roundworms, lungworms, mites, lice and hornflies. 1) Originating from a single Japanese soil sample and the outcome of the innovative, international collaborative research partnership to find new antiparasitics, the extremely safe and more effective avermectin derivative, ivermectin, was initially introduced as a commercial product for Animal Health in 1981. 7) Despite decades of searching around the world, the Japanese microorganism remains the only source of avermectin ever found.
It also has extensive uses in agriculture. It is so useful and adaptable that it is also being used off-label, sometimes, illegally, for example to treat fish lice in the aquaculture industry, where it can have a negative impact on non-target organisms. The ‘Blockbuster’ drug in the Animal Health sector, meaning that it achieved annual sales in excess of over US$1 billion, maintained that status for over 20 years.
15) In referring to the international efforts to tackle Onchocerciasis in which ivermectin is now the sole control tool, the UNESCO World Science Report concluded, “the progress that has been made in combating the disease represents one of the most triumphant public health campaigns ever waged in the developing world”. Inc., and the Public Sector Kitasato Institute in Tokyo, aided by an extraordinary coalition of multidisciplinary international partners and disease-affected communities, has been recognized by many experts and observers as one of the greatest medical accomplishments of the 20th century. Indeed, the discovery, development and deployment of ivermectin, produced by an unprecedented partnership between the Private Sector pharmaceutical multinational Merck & Co.
These move through the body, and when they die they cause a variety of conditions, including skin rashes, lesions, intense itching, oedema and skin depigmentation (Fig. After mating, female worms can release up to 1000 microfilariae a day for some 10–14 years. In the human body, immature larval forms of the parasite create nodules in subcutaneous tissue, where they mature into adult worms. The parasites are transmitted via the bite of infected blackflies of the genus Simulium, which breed in highly-oxygenated, fast-flowing rivers and watercourses.
The programme covered 1.2 million km 2, protecting 30 million people in 11 countries from River Blindness.For over a decade, OCP operations were exclusively based on the spraying of insecticides by helicopters and aircraft over the breeding sites of vector blackflies in order to kill their larvae. In 1974, following international recognition of the dramatic consequences of disabling and disfiguring Onchocerciasis in Africa, four United Nations agencies, including the World Bank, launched the Onchocerciasis Control Programme in West Africa (OCP). 19)By 1973, Onchocerciasis had been recognised by the then head of the World Bank, Robert McNamara, as a major disease of massive health and socioeconomic importance and one in dire need of combating in West Africa, and he became the key agent for change. Communities in these areas exhibited high rates of visual disability caused by Onchocerciasis, up to 40% in some areas, which caused immeasurable negative impact on individual and community health, reducing economic capacity and productivity, and leading to the abandonment of fertile agricultural lands.
Inc., to treat onchocerciasis in all endemic countries for as long as it was needed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
